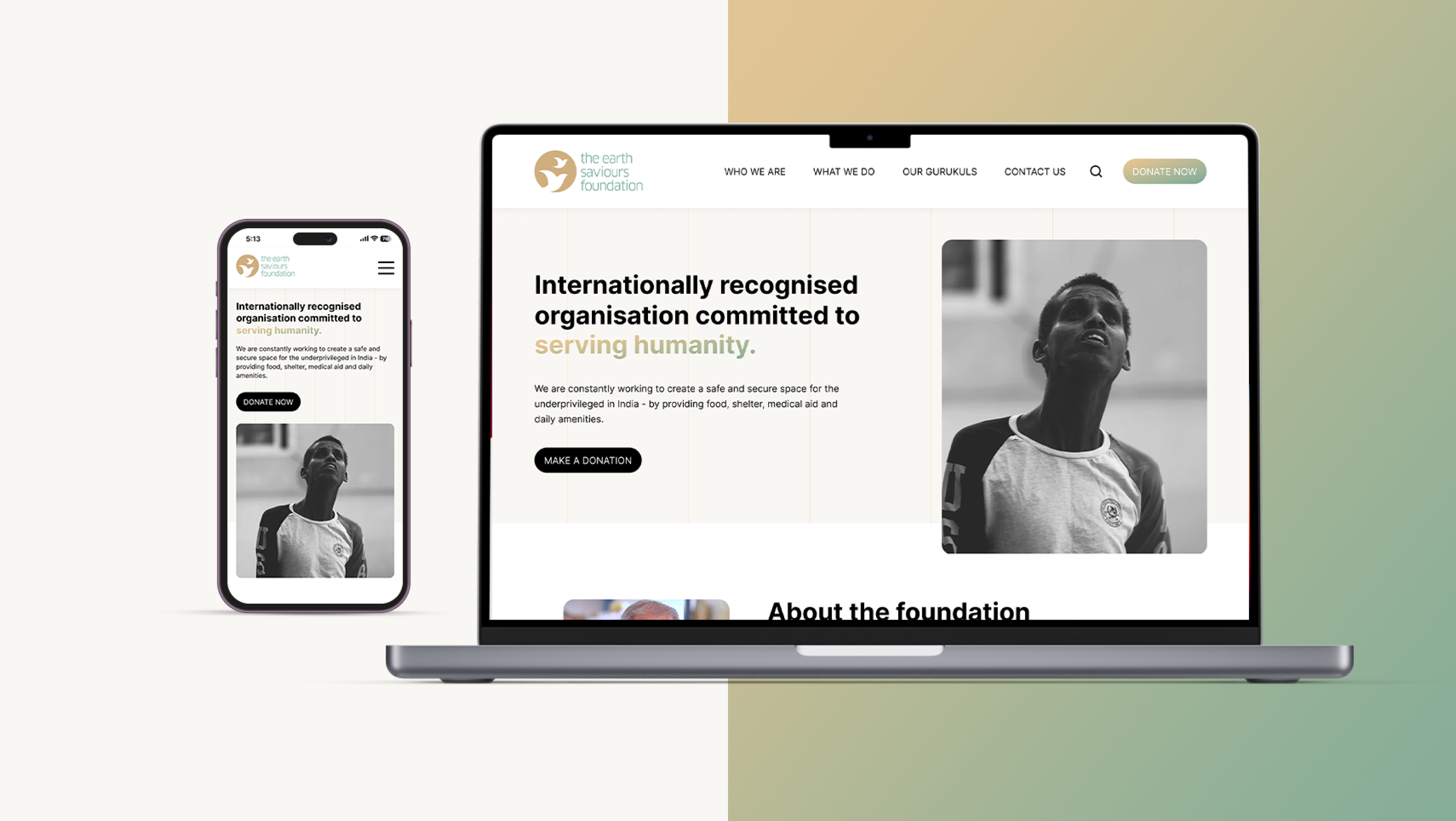
Service Design | Climate Change | Interaction Design | Learning through Play
The Problem
Anthropogenic climate change is rendering hydro-meteorological disasters, such as rainfall, storms, and floods, increasingly unpredictable, frequent, and intense in India. The repercussions of these phenomena are distinctly experienced by economically marginalised communities in urban areas. Compounding the issue, the compartmentalised approach of government, urbanisation and disaster management bodies often results in the neglect of these communities residing in informal settlements at the administrative level. Consequently, there is an imperative to empower community members with awareness and a sense of ownership in order to undertake anticipatory actions that can effectively mitigate the risks and adverse consequences of these disasters.
Anthropogenic climate change is rendering hydro-meteorological disasters, such as rainfall, storms, and floods, increasingly unpredictable, frequent, and intense in India. The repercussions of these phenomena are distinctly experienced by economically marginalised communities in urban areas. Compounding the issue, the compartmentalised approach of government, urbanisation and disaster management bodies often results in the neglect of these communities residing in informal settlements at the administrative level. Consequently, there is an imperative to empower community members with awareness and a sense of ownership in order to undertake anticipatory actions that can effectively mitigate the risks and adverse consequences of these disasters.
The Service
This service focuses on exploring the impact of floods in urban India, with a specific emphasis on the vulnerable communities in Delhi NCR. The deliverable in form of a hopscotch game has been created as a key component, designed to facilitate community engagement and dialogue. It can be facilitated by volunteering training agencies such as NGOs or disaster management consultancies, such as in this case, Zone4Solution, a Delhi-based organisation training communities and critical infrastructures’ residents about disaster preparedness.
Framework & Functionality
The service is designed keeping in mind the design justice framework (2018) while the interaction of the game including the questions and their flow are implemented through the UNDRR’s four pillars of Multi-Hazard Early Warning System (WMO, 2022) and the futures triangle (Inayatullah, 2008) respectively in order to establish the interactive and collaborative game into the service. This builds the experience design of the game encouraging disaster preparedness, awareness and articulation of risks and safety for communities and a human centred design approach through understanding the community’s needs by the volunteering agencies - overall bridging the gaps between local governments & authorities and urban poor communities.
The service is designed keeping in mind the design justice framework (2018) while the interaction of the game including the questions and their flow are implemented through the UNDRR’s four pillars of Multi-Hazard Early Warning System (WMO, 2022) and the futures triangle (Inayatullah, 2008) respectively in order to establish the interactive and collaborative game into the service. This builds the experience design of the game encouraging disaster preparedness, awareness and articulation of risks and safety for communities and a human centred design approach through understanding the community’s needs by the volunteering agencies - overall bridging the gaps between local governments & authorities and urban poor communities.
Frugal Innovation
In a resource poor environment with limited budgets from partnering organisations, bricolage (enabling people to explore existing resources in novel ways where material resources are scarce) and frugal innovation (avoiding needless costs on resources when the economic conditions of the potential beneficiaries can’t be changed) play a key role in establishing the physical elements of this game. In both the cases, scarcity is seen as an opportunity (Cunha et al, 2014) to innovate different ways of setting up the Hop4Action grid and playing. The Library of Materials is a collection of suggested everyday objects offered with the game instructions for beneficiaries and facilitators to make use of available resources instead of burdening themselves with resource costs.
Mapping the system to highlight the gaps between the stakeholders that may be directly involved, I identified the area of intervention and therefore developed the service through an iterative process. Research methods included workshops, surveys, interviews and co-design sessions, further iterating the game into a final service deliverable through prototyping and testing - as shown above.
Conclusion
By leveraging collective intelligence and the narrative of past experiences, present actions, and future vision, the project aims to enhance awareness and preparedness for potential flooding. The incorporation of climate justice, anticipatory action, and design justice framework reflects a comprehensive approach to address the vulnerabilities of these communities. The collaboration with experts in climate change, disaster management, and urban planning, along with user interviews and rigorous testing, underscores the depth of research and consideration that went into its development. The decision to potentially make the project an open-source game and toolkit on the Zone4Solution website enhances its scalability and potential impact on a broader scale. The reflections highlight the evolution of the project, emphasising the importance of simplicity, accessibility, and resilience in its design. Overall, this initiative holds promise in fostering climate adaptation and resilience among vulnerable groups, ultimately contributing to more proactive disaster foresight and preparedness.
READ THE FULL REPORT HERE
THANK YOU